fetchDiffCorrGrinnNetwork
This example shows how to compute a differential correlation network and expand the network with information from Grinn internal database
- INPUT
The table summarizes important arguments
Argument Value Description datX1 data frame containing normalized-omic data of one condition Columns correspond to entities e.g. genes and rows to samples. Require 'nodetype' at the first row to indicate the type of entities in each column. datX2 data frame containing normalized-omic data of another condition It uses the same format as datX1. datY1 data frame containing normalized-omic data of one condition It uses the same format as datX1. Or it can be NULL, if there is only one omic data type datY2 data frame containing normalized-omic data of another condition It uses the same format as datX1. Or it can be NULL, if there is only one omic data type pDiff numerical value The maximum pvalues (pvalDiff), to include edges in the output xTo entity type e.g. metabolite The correlation network can be expanded from datX entites to a specific entity type, by providing a value to sourceTo yTo entity type e.g. gene The correlation network can be expanded from datY entites (if not NULL) to a specific entity type, by providing a value to yTo - EXECUTE FUNCTION
Compute a differential correlation network of metabolites in normal and cancer tissue and expand to the grinn network of metabolite-gene
#1. load metabolomics data from a csv file datMet = read.csv("Lung_MET.csv", header=TRUE, row.names=1, stringsAsFactors=FALSE) #2. show dimensions of metabolomics data dim(datMet) #3. show the first 10 rows and 10 columns datMet[1:10,1:10] #!!--- NOTE: The following codes convert kegg ids to grinn ids. If the input data is already the grinn ids, these steps can be skipped. grinnID = convertToGrinnID(txtInput=colnames(datMet), nodetype="metabolite", dbXref="kegg") #call grinn function to convert ids grinnID = grinnID[!duplicated(grinnID[,1]),] #keep the first mapped id colnames(datMet) = lapply(colnames(datMet),function(x) ifelse(length(which(grinnID$FROM_kegg == x))>0,as.character(grinnID$GRINNID[which(grinnID$FROM_kegg == x)]),x)) #---------- END id conversion ----------# datMetNormal = datMet[1:40,] #normal condition datMetTumor = rbind(nodetype=rep("metabolite"),datMet[41:79,]) #tumor condition result <- fetchDiffCorrGrinnNetwork(datX1=datMetNormal, datX2=datMetTumor, pDiff=1e-4, method="spearman", returnAs="tab", xTo="gene") #display the first 10 edgelists result$edges[1:10,] datMet2 = datMet[c(1:7,42:50),] datMetNormal = datMet2[1:7,] datMetTumor = rbind(nodetype=rep("metabolite"),datMet2[8:13,]) datGeneNormal = datGene[1:7,] datGeneTumor = rbind(nodetype=rep("gene"),datGene[8:13,]) result <- fetchDiffCorrGrinnNetwork(datX1=datMetNormal, datX2=datMetTumor, datY1=datGeneNormal, datY2=datGeneTumor, pDiff=1e-5, method="spearman", returnAs="tab", xTo="protein", yTo="pathway") - EXPORT OUTPUT
Export the network as tab-delimited files to visualize in Cytoscape
write.table(as.matrix(result$edges),"diffcorrNwEdge.txt",sep="\t",row.names = F, quote = FALSE) write.table(as.matrix(result$nodes),"diffcorrNwNode.txt",sep="\t",row.names = F, quote = FALSE) - VISUALIZATION
The figure is generated by Cytoscape 3.1.1 using grinn style (grinn.xml). It is corresponding to the cytoscape file diffcorrNw.cys.
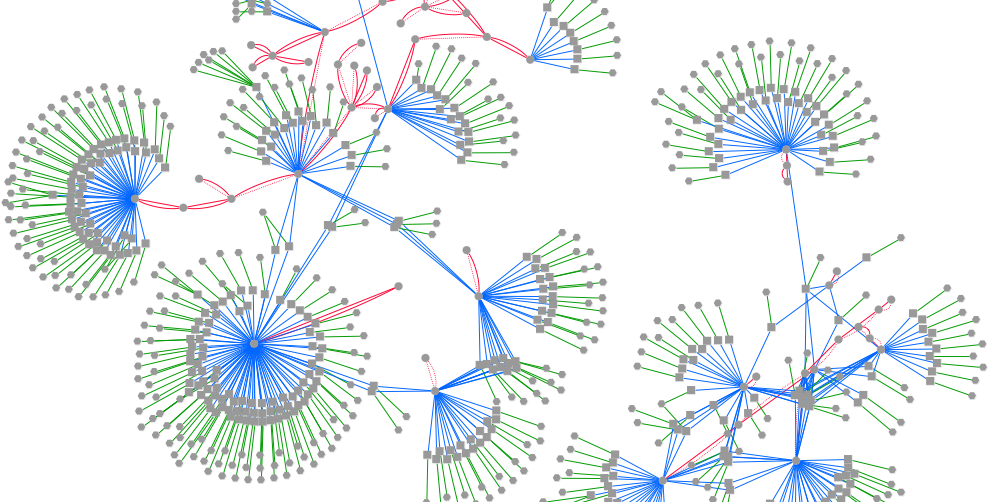
Diagram legend
References
Correlation-based analysis apply the Fisher's z-test method from the following publication:
- Fukushima A DiffCorr: an R package to analyze and visualize differential correlations in biological networks. Gene 2013;10;518(1):209-14.
Metabolomics data used in this example are taken from the following publication:
- Wikoff WR, et al. Metabolomic markers of altered nucleotide metabolism in early stage adenocarcinoma. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2015;8(5):410-8.
Go to HOME | Documentation | fetchGrinnNetwork | fetchCorrGrinnNetwork | fetchDiffCorrGrinnNetwork | fetchModuGrinnNetwork | fetchGrinnCorrNetwork | input formats
 View on GitHub
Download .zip
Download .tar.gz
View on GitHub
Download .zip
Download .tar.gz